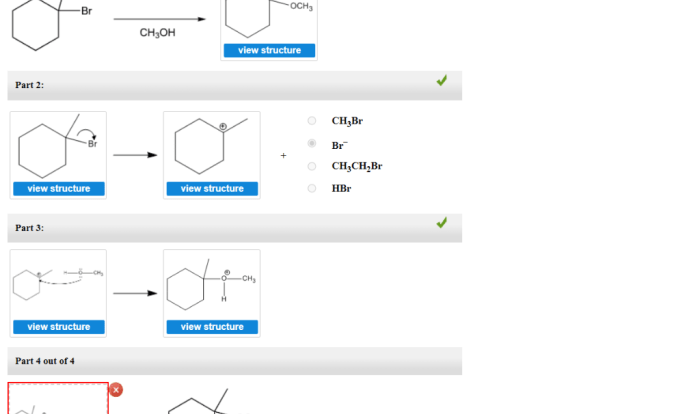
Draw the major organic product for the friedel-crafts acylation reaction – The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is a versatile and powerful method for introducing acyl groups into aromatic rings. This reaction has wide applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and fragrances. Understanding the regioselectivity and orientation of the reaction is crucial for predicting the major organic product.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, exploring its mechanism, regioselectivity, reaction conditions, and synthetic applications. We will also provide practical tips for drawing the major organic product of this reaction.
Introduction: Draw The Major Organic Product For The Friedel-crafts Acylation Reaction
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is a powerful method for introducing acyl groups into aromatic rings. It is a versatile reaction that can be used to synthesize a wide variety of organic compounds, including ketones, aldehydes, and esters.
The general mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction involves the electrophilic addition of an acyl chloride or anhydride to an aromatic ring. The reaction is catalyzed by a Lewis acid, such as aluminum chloride or iron(III) chloride. The Lewis acid activates the acyl chloride or anhydride by coordinating to the carbonyl oxygen, which makes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic.
The electrophilic carbonyl carbon then attacks the aromatic ring, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. The product of the reaction is a ketone or an aldehyde, depending on the starting materials used.
Regioselectivity and Orientation
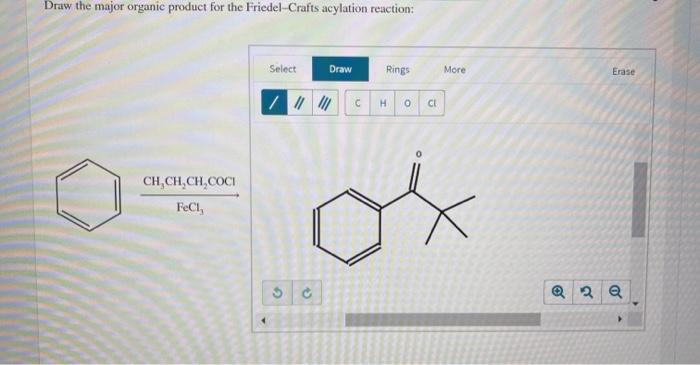
The regioselectivity of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is determined by the electronic properties of the aromatic ring. Acyl groups are preferentially added to positions on the aromatic ring that are activated by electron-donating groups, such as alkyl groups or alkoxy groups.
The orientation of the acyl group is also influenced by the electronic properties of the aromatic ring. Acyl groups are preferentially added to positions on the aromatic ring that are ortho or para to electron-donating groups.
Reaction Conditions
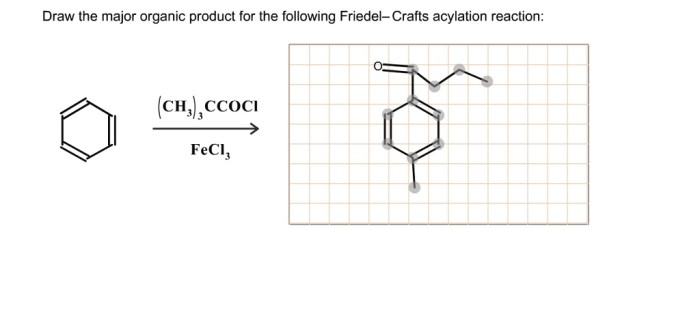
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is typically carried out in a solvent, such as dichloromethane or nitrobenzene. The reaction temperature can vary depending on the starting materials used, but it is typically in the range of 0 to 100 °C.
The catalyst used in the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is typically a Lewis acid, such as aluminum chloride or iron(III) chloride. The Lewis acid activates the acyl chloride or anhydride by coordinating to the carbonyl oxygen, which makes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic.
Applications
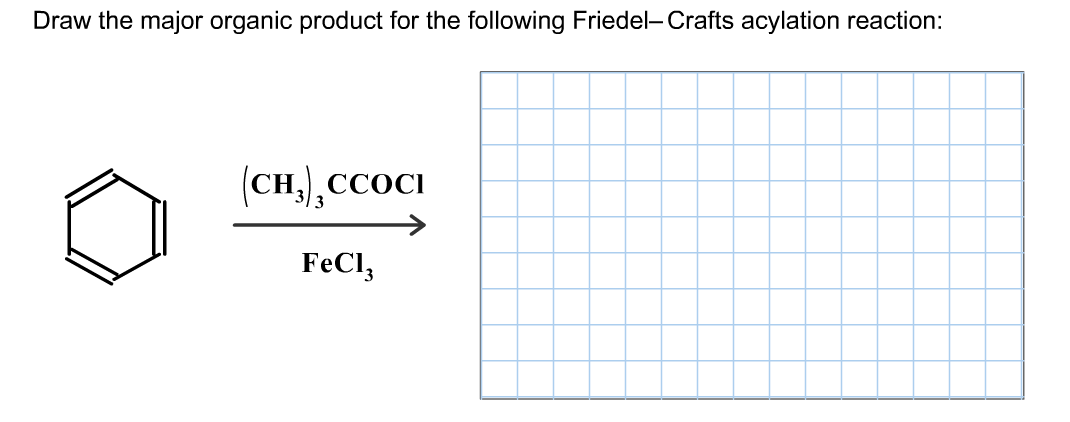
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is a versatile reaction that can be used to synthesize a wide variety of organic compounds. Some of the most common applications of the reaction include the synthesis of ketones, aldehydes, and esters.
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is also used in the synthesis of more complex organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and dyes.
FAQ Overview
What is the mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction proceeds via an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism. The electrophile is the acyl cation, which is generated from the reaction of an acyl chloride with a Lewis acid catalyst.
What factors influence the regioselectivity of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
The regioselectivity of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is influenced by several factors, including the electronic properties of the aromatic ring, the steric hindrance of the substituents on the aromatic ring, and the reaction conditions.
What are the typical reaction conditions for the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is typically carried out in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as aluminum chloride or iron(III) chloride. The reaction is typically performed in a non-polar solvent, such as dichloromethane or carbon disulfide.