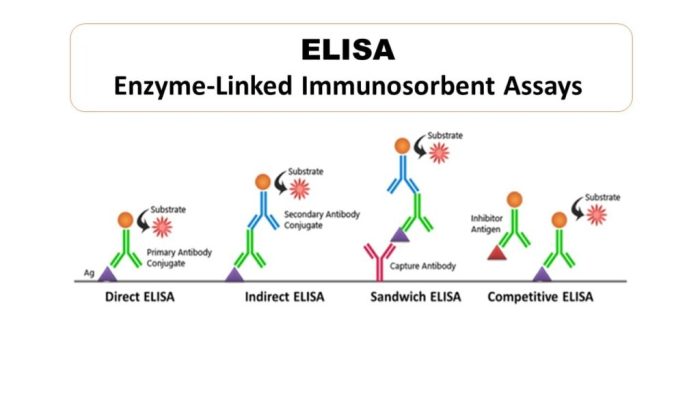
Choose the statement that best describes the direct elisa technique – The direct ELISA technique, an indispensable tool in the realm of immunoassays, stands out for its simplicity and versatility. This technique, which employs antibodies directly conjugated to an enzyme, offers a straightforward and sensitive approach for detecting and quantifying antigens in various biological samples.
Its applications span a wide range of fields, including research, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.
The direct ELISA technique involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps. First, the antigen of interest is immobilized on a solid surface, such as a microplate. Next, a primary antibody specific to the target antigen is introduced, forming an antigen-antibody complex.
The primary antibody is directly conjugated to an enzyme, which serves as a reporter molecule. In the final step, a substrate is added, and the enzyme catalyzes a colorimetric or fluorometric reaction, generating a quantifiable signal proportional to the amount of antigen present.
Direct ELISA Technique
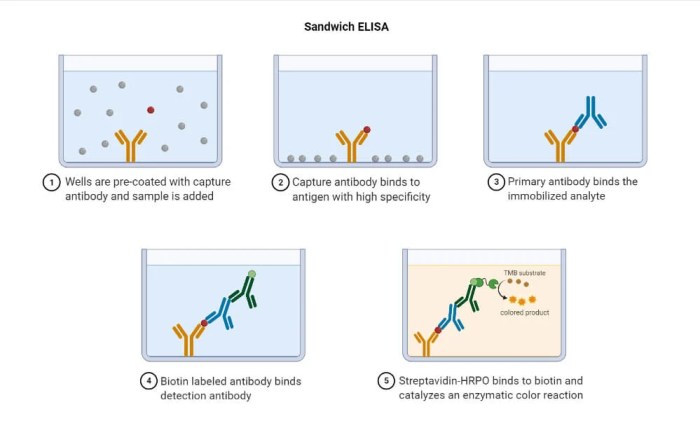
The direct ELISA technique is a highly sensitive and specific immunoassay used for the qualitative and quantitative detection of antigens or antibodies in a sample. It is a widely employed technique in various fields of research, diagnostics, and biotechnology.
Components and Procedure
The direct ELISA technique involves the use of:
- Antigen-coated microplate
- Antibody-enzyme conjugate
- Substrate
- Chromogenic or fluorogenic reagents
The procedure consists of:
- Coating the microplate with the antigen
- Incubating the sample with the antibody-enzyme conjugate
- Washing the unbound conjugate
- Adding the substrate
- Measuring the absorbance or fluorescence of the reaction product
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Rapid and easy to perform
- Versatile and can be adapted to various analytes
Disadvantages:
- Cross-reactivity can occur
- Limited dynamic range
- Can be time-consuming
Applications
The direct ELISA technique has a wide range of applications, including:
- Detection of infectious agents (e.g., viruses, bacteria)
- Quantification of hormones and cytokines
- Determination of antibody titers
- Food safety and environmental monitoring
Comparison to Indirect ELISA, Choose the statement that best describes the direct elisa technique
The direct ELISA technique differs from the indirect ELISA technique in that the antibody used in the direct ELISA is directly labeled with an enzyme. This eliminates the need for a secondary antibody and reduces the risk of non-specific binding.
Optimization and Troubleshooting
Factors that can affect the performance of the direct ELISA technique include:
- Antigen coating concentration
- Antibody-enzyme conjugate concentration
- Incubation time and temperature
- Washing efficiency
Troubleshooting tips for common problems encountered in the direct ELISA technique include:
- High background signal: Optimize washing steps and reduce antibody-enzyme conjugate concentration
- Low signal: Increase antigen coating concentration or antibody-enzyme conjugate concentration
- Cross-reactivity: Use highly specific antibodies or employ blocking agents
Essential FAQs: Choose The Statement That Best Describes The Direct Elisa Technique
What is the primary advantage of the direct ELISA technique?
The direct ELISA technique offers several advantages, including its simplicity, sensitivity, and versatility. It requires fewer steps and reagents compared to indirect ELISA, making it more straightforward and cost-effective.
What are some limitations of the direct ELISA technique?
One limitation of the direct ELISA technique is the potential for cross-reactivity, where the antibody may bind to non-target antigens. Additionally, the sensitivity of the technique can be affected by factors such as the affinity of the antibody and the efficiency of the enzyme conjugation.