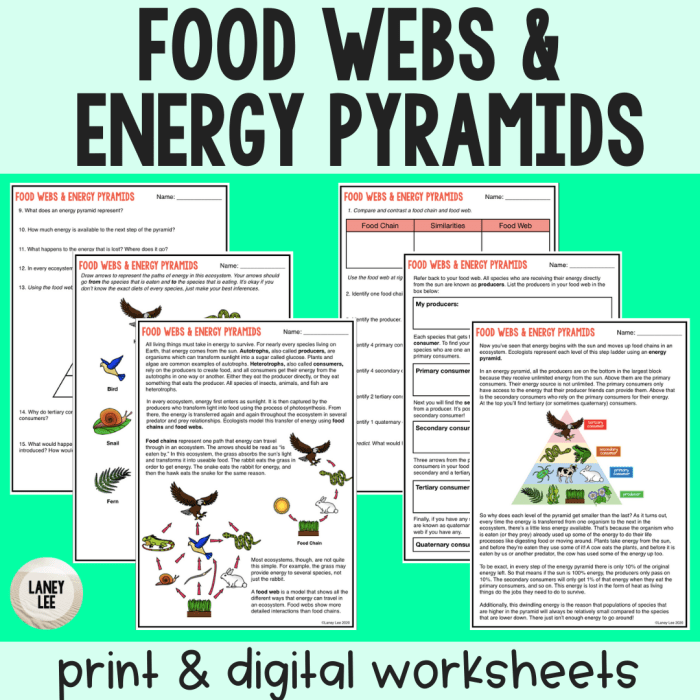
Food chain food webs and energy pyramid worksheet – Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive worksheet on food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. This meticulously crafted resource delves into the intricate relationships within ecosystems, unraveling the flow of energy and the interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of food chains, unraveling the linear sequence of organisms that transfer energy through consumption. Explore the complex dynamics of food webs, where multiple interconnected food chains coexist, showcasing the intricate dependencies and interrelationships within ecosystems.
Food Chains: Food Chain Food Webs And Energy Pyramid Worksheet
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass, starting with a producer organism and ending with a top predator.
Examples:
- Grass → Grasshopper → Snake → Hawk
- Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fish → Shark
Roles in a Food Chain:
- Producers:Autotrophic organisms that convert inorganic matter into organic compounds through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Consumers:Heterotrophic organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
- Decomposers:Organisms that break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
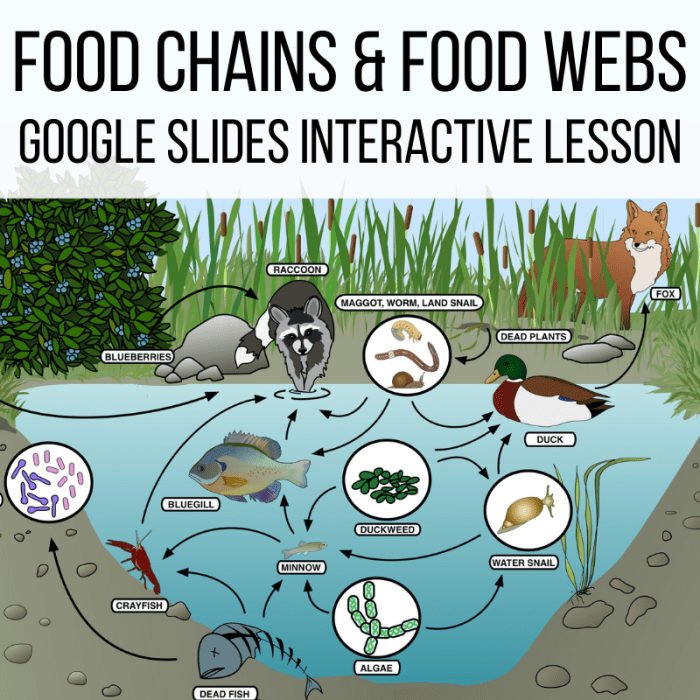
Food Webs
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains, representing the feeding relationships among multiple species within an ecosystem.
Differences from Food Chains:
- More complex and interconnected.
- Multiple pathways for energy flow.
- Resilient to changes in the population of a single species.
Diagram of a Food Web:
Producers (e.g., plants) → Primary consumers (e.g., herbivores) → Secondary consumers (e.g., carnivores) → Tertiary consumers (e.g., top predators)
Interconnections and Dependencies:
Species within a food web rely on each other for food and energy, forming intricate and interdependent relationships.
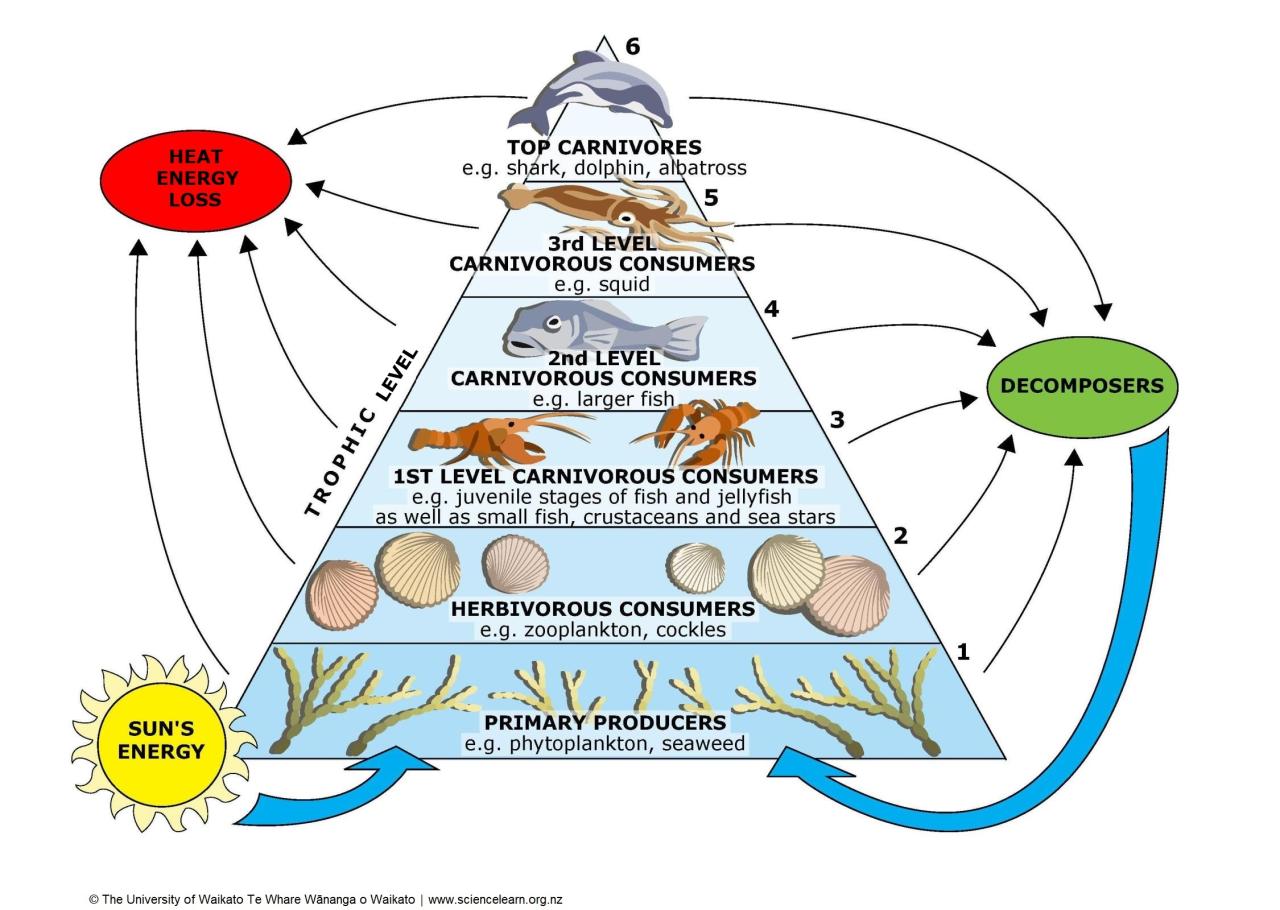
Energy Pyramids
An energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the amount of energy available at each trophic level within an ecosystem.
Shape:
- Typically triangular, with the base representing producers and the apex representing top predators.
- Each level represents approximately 10% of the energy available at the level below.
Example:
- Level 1: Producers (1000 kcal)
- Level 2: Primary consumers (100 kcal)
- Level 3: Secondary consumers (10 kcal)
- Level 4: Tertiary consumers (1 kcal)
Energy Transfer and Loss:
Energy is lost at each trophic level due to metabolic processes, heat dissipation, and waste production.
Worksheet Activities
Exercises on Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramids:
- Create a food chain for a local ecosystem.
- Construct a food web diagram based on a given scenario.
- Analyze an energy pyramid and discuss the implications of energy loss.
Table Comparing Food Chains and Food Webs:
| Characteristic | Food Chain | Food Web |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear | Complex and interconnected |
| Energy Flow | Single pathway | Multiple pathways |
| Resilience | Less resilient | More resilient |
Section for Analyzing and Interpreting Energy Pyramids:
- Identify the trophic levels and energy values.
- Calculate the percentage of energy lost at each level.
- Discuss the ecological implications of energy loss.
Query Resolution
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain represents a linear sequence of organisms, while a food web depicts the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem, where multiple food chains overlap and interact.
How do energy pyramids illustrate energy flow in ecosystems?
Energy pyramids graphically represent the amount of energy available at each trophic level, demonstrating the progressive loss of energy as it moves up the food chain.
What is the role of decomposers in food chains and food webs?
Decomposers break down dead organisms and waste products, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem and completing the cycle of energy flow.