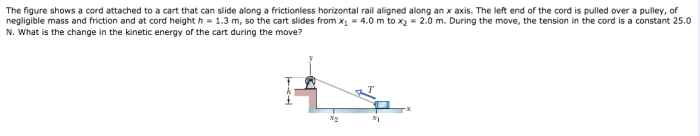
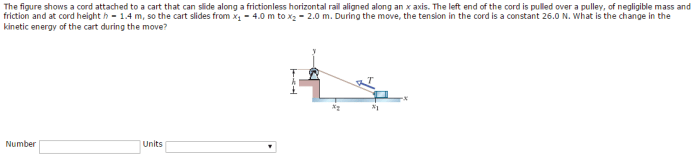
The figure shows a cord attached to a cart, inviting us on an exploration of the intriguing dynamics that govern this seemingly simple system. This investigation promises to illuminate the interplay of forces, energy, and motion, revealing the practical implications and potential applications of this fundamental setup.
Delving into the physical characteristics of the cord and cart, we will examine their composition, dimensions, and the nature of their attachment. The cord’s material properties, such as flexibility, elasticity, and tensile strength, will be scrutinized for their influence on the system’s behavior.
Cord and Cart System: The Figure Shows A Cord Attached To A Cart
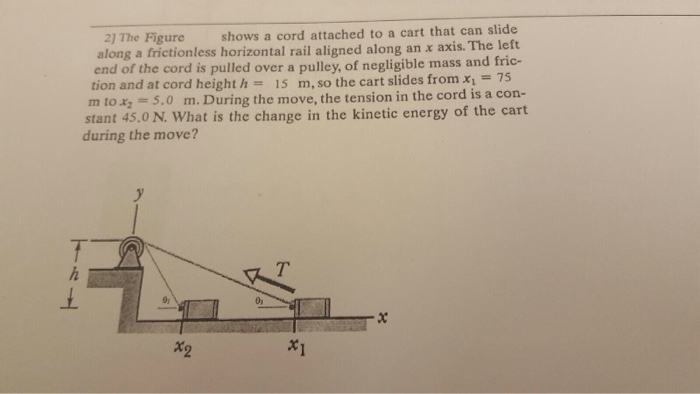
This system consists of a flexible cord attached to a cart. The cord is typically made of a durable material such as nylon or polyester, and its properties influence the system’s dynamics.
Cord Properties
- Material Composition:The cord is composed of a strong, flexible material that can withstand tension and deformation.
- Flexibility:The cord is highly flexible, allowing it to be easily bent and manipulated without breaking.
- Elasticity:The cord exhibits elasticity, enabling it to stretch and return to its original length when the tension is released.
- Tensile Strength:The cord possesses high tensile strength, allowing it to withstand significant pulling forces without breaking.
Cart Dynamics
When the cord is taut, the cart experiences a pulling force that causes it to accelerate. The acceleration of the cart depends on the tension in the cord and the mass of the cart.
- Forces on the Cart:The cart is subject to the pulling force from the cord, as well as friction and air resistance.
- Acceleration:The acceleration of the cart is directly proportional to the tension in the cord and inversely proportional to the mass of the cart.
- Potential Energy:When the cord is stretched, it stores potential energy that is converted into kinetic energy as the cart accelerates.
System Interactions, The figure shows a cord attached to a cart
The tension in the cord plays a crucial role in the cart’s movement. Changes in cord tension directly affect the acceleration and behavior of the cart.
- Tension-Acceleration Relationship:The tension in the cord determines the acceleration of the cart. Higher tension results in greater acceleration.
- Cord Tension Limitations:The cord has a maximum tension capacity beyond which it may break or become damaged.
Applications and Implications
Cord-and-cart systems have numerous applications in various fields:
- Engineering:Design of pulleys, winches, and other lifting mechanisms.
- Physics:Understanding the principles of motion, energy conservation, and force.
- Sports:Analysis of projectile motion in activities such as archery and javelin throw.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of the cord’s material composition?
The material composition of the cord influences its flexibility, elasticity, and tensile strength, which in turn affect the system’s dynamics. A more flexible cord will allow for greater deformation under tension, while a stronger cord will withstand higher forces before breaking.
How does the tension in the cord affect the cart’s motion?
The tension in the cord exerts a force on the cart, causing it to accelerate. The greater the tension, the greater the acceleration. However, if the tension exceeds the cord’s tensile strength, the cord will break, and the cart will no longer be constrained.